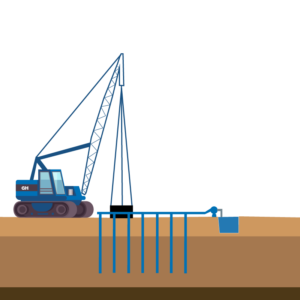
Ground Improvement
Ground improvement is the process of modifying the physical, chemical, and mechanical properties of soil to create a more stable foundation for construction. This can be achieved through various methods.
Consolidation methods
- Vacuum Consolidation Method (VCM)
The Vacuum Consolidation Method (VCM) is utilized for improving soft ground by employing atmospheric pressure as a temporary surcharge for soil consolidation.
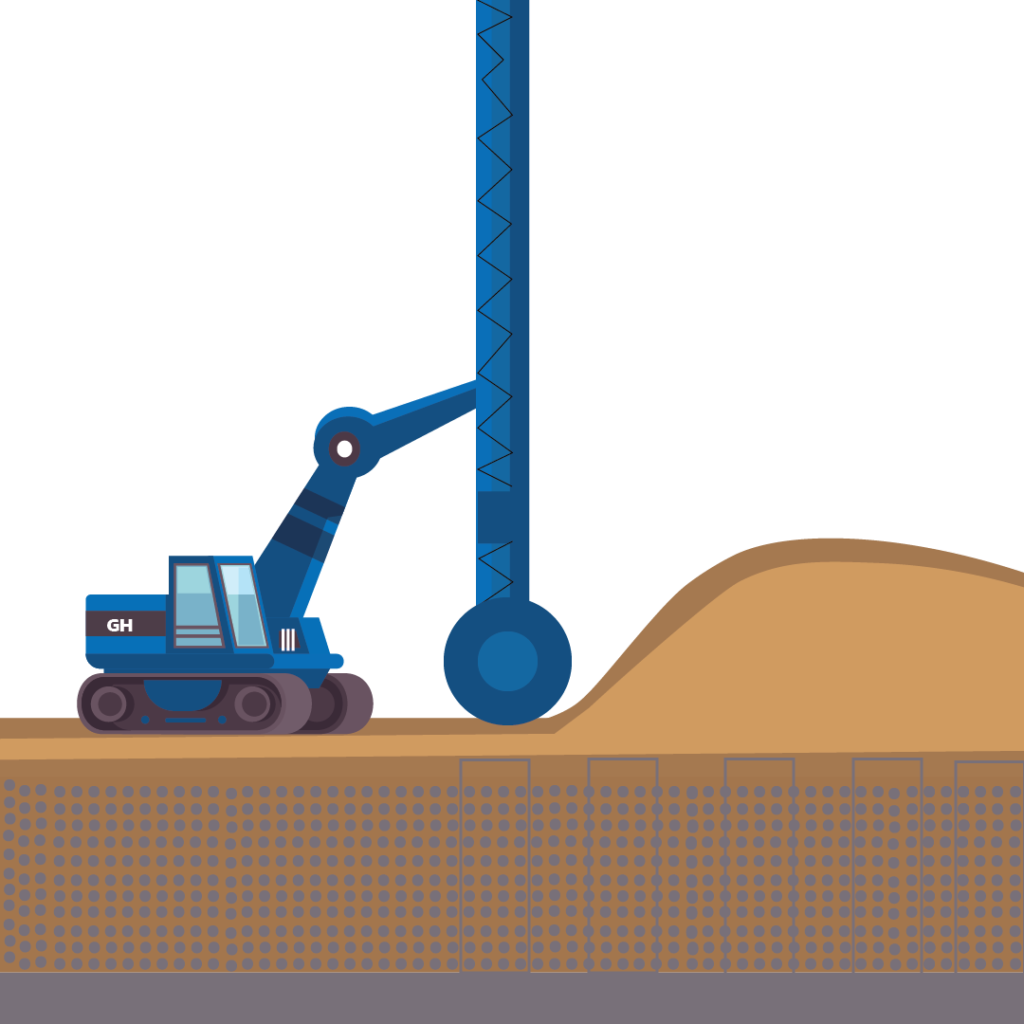
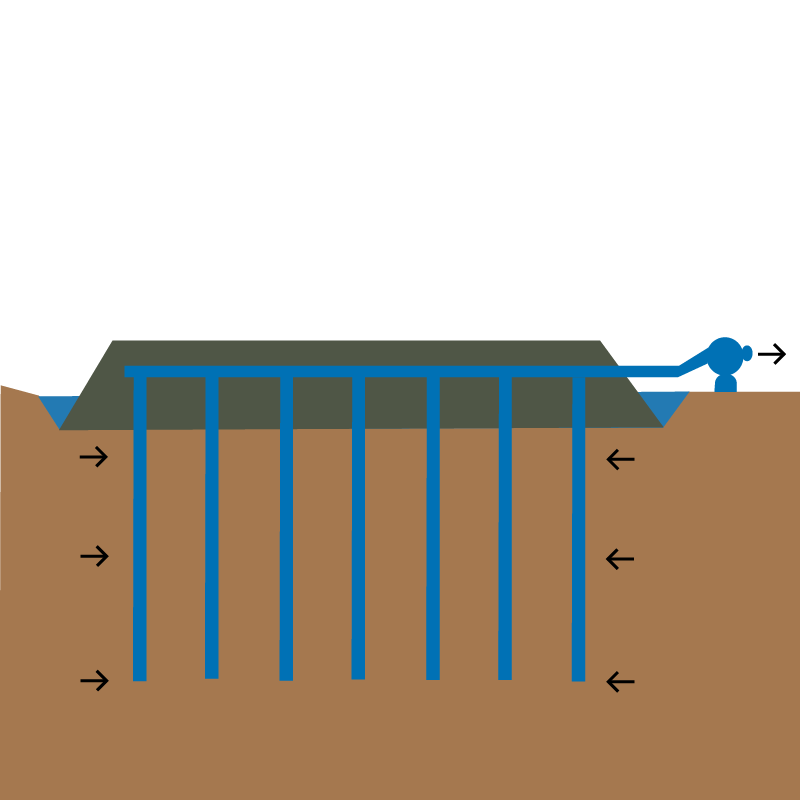
Reinforcement methods
- Deep Cement Mixing (DCM)
Suitable for improving in-situ soft soil strength, such as clays, peats, and other weak soils, by mechanically mixing them with a cementitious binder.
- Jet Grout Column
One semi-rigid inclusion method, the high-velocity water-cement paste, involves injecting it through horizontal nozzles, breaking down the soil matrix. The jet erodes and mixes the in-situ soil with grout, rotating upward to form a soil-cement composite mixture.


Densification methods
- Dynamic Replacement (DR)
is an extension of Dynamic Compaction (DC) where cohesionless soils are replaced, after compaction, with large granular columns.
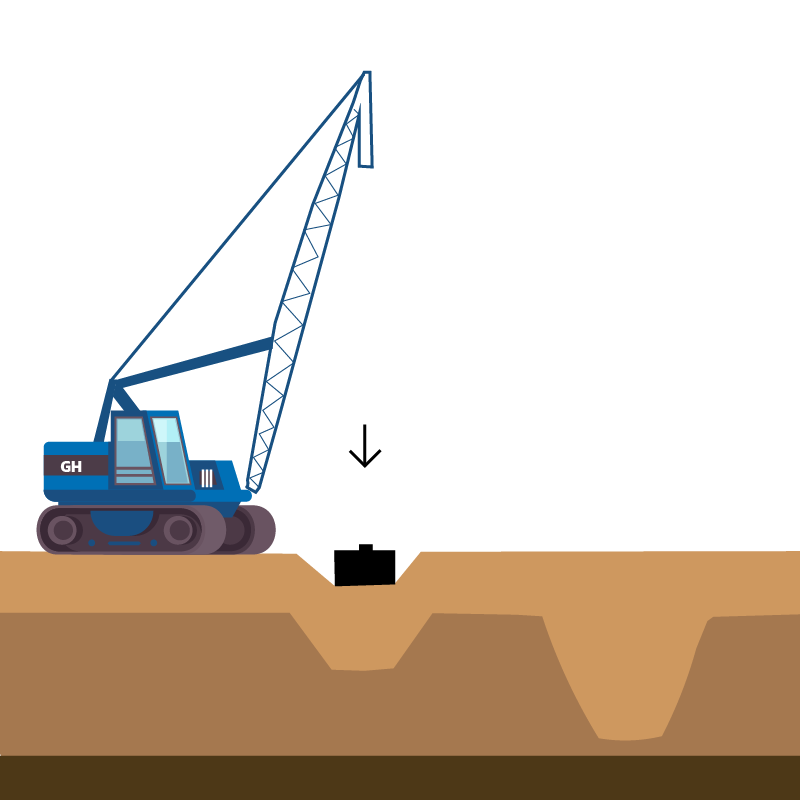
- Dynamic compaction (DC)
is a ground improvement technique that densifies soils by repeated surface tamping using a heavy steel drop weight.
- Vibro-replacement (Stone/ Sand Column)
An extension of Vibro Compaction involves replacing cohesionless soils, after compacting, with large granular columns.
- Vibro Compaction
A method to stabilize or compact the deep layers of non-cohesive soils, suitable to compact loose, granular soils to mitigate liquefaction and reduce settlement, extremely effective in free draining granular soils.
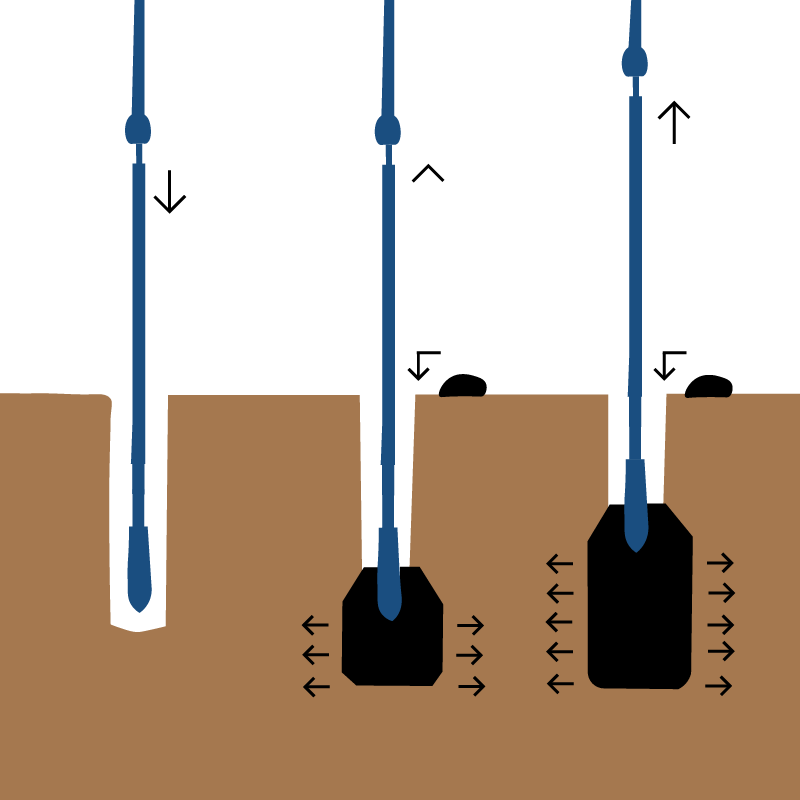
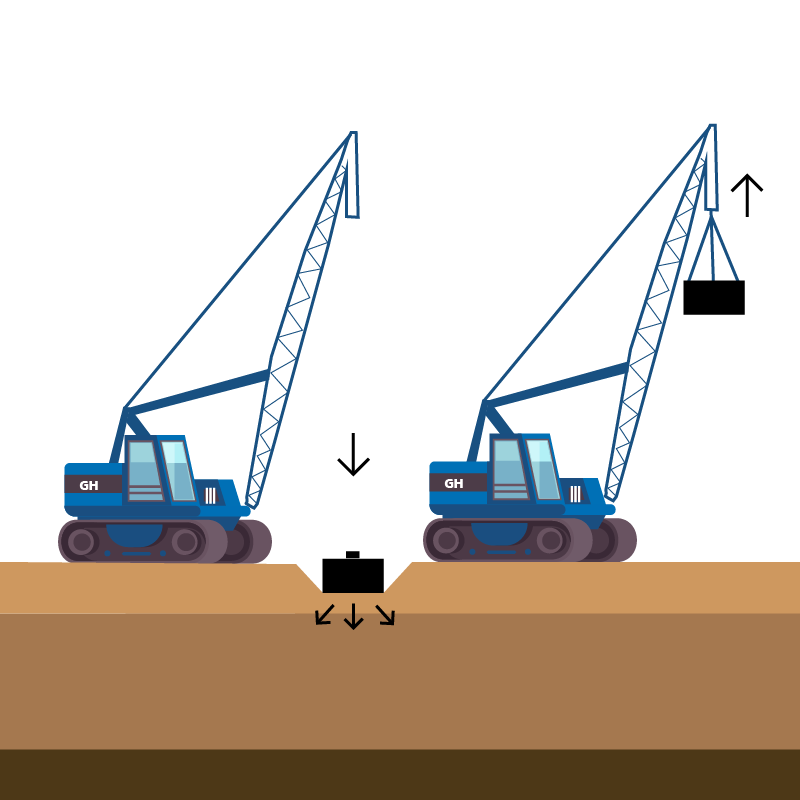
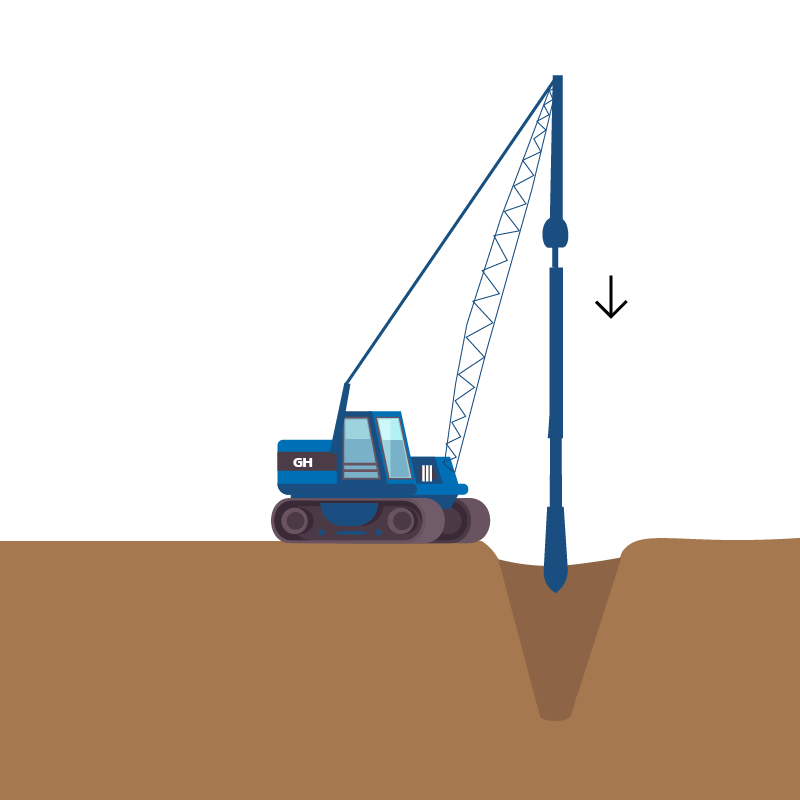
- High Vacuum Densification Method (HVDM)
is an advanced method for improving the physical properties of materials. It involves the application of high vacuum pressure to a material in order to decrease its porosity and increase its density.